With the rise of new technologies, cybersecurity has become a top concern for all companies. The future of cybersecurity is dependent on how many people are going to be using the internet and how much data they are going to be sharing.
The more connected we become, the greater our need for cybersecurity becomes.
Companies that invest in human resources will have a better chance of succeeding. It is easier to protect your online data when you have a large team of people who know how to safeguard it.
There are two ways to approach this problem:
- Either you can invest in technology that can keep up with the changing environment or
- You can invest in human resources that know how to protect themselves and their company’s data.
What is the Future of Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity presents an opportunity for every person in your company to learn how they can be better prepared for cyberattacks by educating themselves on what you need and what you could be doing better.
The impact of cybersecurity on the future is immeasurable. It is a problem that has been escalating in severity and size since it began, and there will be no escaping it until it is stopped.
The amount of data that is being collected by the government has risen dramatically in the past several decades.
The problem with this is that there is a large amount of information on private citizens, and no regulation exists on how to handle this information. Currently, American companies are not held responsible for the use of their technology makes of personal data.
This creates a problematic situation where companies may use your data without proper consent. In order to create a sustainable future, people need to be educated on the impact of cyber-terrorism and cyberattacks.
Ever wonder what the future of cybersecurity by 2030 will look like? While 6 years might seem a long way into the future, the speed at which the industry is developing is sure to make the next decade fly by.
Forecasting the future of cybersecurity isn’t about looking into the crystal ball simply for fun.
By envisioning how cybersecurity will change in the next few years, big companies and security professionals can prepare for potential challenges, so they don’t look back and hope they had acted in 2023.
No one can tell accurately what the next main cyber threat will be or where it will come from, but professionals still have an excellent idea of the general direction that we’re heading in.
With cybercrime on the rise, experts that need for Cybersecurity bootcamps is greater than ever in shaping the professionals to tackle advanced persistent threats (APTs), which are large-scale, politically motivated attacks.
Though tomorrow is never assured, paying attention to the cybersecurity predictions listed below will assist you in future-proof your business & other online activities.
Cybersecurity Trends and Predictions for 2025
- Regulation of Cybersecurity in AI Development.
- Cybersecurity in Space: Protecting Satellites and Space Infrastructure.
- Decentralized Identity and Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI).
- Rise of Cyber Insurance Fraud.
- Zero Trust Will Become the Standard Security Model.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and Targeted Attacks.
- Expansion of Zero Trust Architecture.
- Quantum Computing Threats and Post-Quantum Cryptography.
Cybersecurity Outlook for 2024
- Poorly developed generative AI apps pose a security risk.
- Deepfakes could be used for impersonation.
- Chatbots can be hijacked to steal data.
- Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) simplifies attacks.
- Phishing and social engineering remain major threats.
- Attacks Against Cloud Services.
- Rise of Automotive Hacking.
Cybersecurity Forecast for 2024

- AI’s Dual Role in Cyber Operations: Enhancing Offense and Defense
- Global Espionage Trends: Focus on China, Russia, North Korea, and Iran
- Rising Threats: Zero-Day Vulnerabilities and Edge Device Targeting
- Cloud-Centric Attacks: Exploiting Misconfigurations and Identity Weaknesses
- Cyber Landscape Shaped by Global Conflicts: Hacktivism, Phishing, and More
- Resurgence of Older Techniques: Overcoming Modern Detection Systems
- Malware Evolution: The Shift to Go, Rust, and Swift Programming Languages
Source: Google Cloud
Cybersecurity Strategic Imperative for 2024
- The cost of cyber attacks on the global economy is predicted to top $10.5 trillion by the end of 2024.
- Soft skills will become increasingly essential for cybersecurity professionals.
- The cybersecurity skills shortage will continue to be a problem in 2024 too.
- Cybersecurity regulations will become more stringent.
- Artificial Intelligence will have a transformative impact on both cyber attack and defense.
- Generative AI will be adopted on both sides of the battle, with attackers using it to create more sophisticated attacks and defenders using it to detect and evade threats.
- Phishing attacks will become more sophisticated, with attackers using deepfakes to make them more believable.
- Cyber resilience will become increasingly important as organizations realize that even the best security can’t guarantee 100% protection.
- Zero trust will move from being a technical network security model to something adaptive and holistic.
- Cyber warfare and state-sponsored cyber attacks will continue to be a threat.
Source: Forbes
Global Cybersecurity Predictions for 2024
- Election security in focus due to past meddling.
- Organizations to embrace AI’s dual nature for defense and threat detection.
- Zero-trust architecture adoption to combat evolving threats.
- APAC cities integrating IoT in critical infrastructure raising vulnerability concerns.
- Supply chain risks necessitate resilience assessments and adaptation.
- Third-party scrutiny intensifies to mitigate vendor risks.
- Stricter Australian regulations with potential fines for inadequate security.
- Individual accountability for cybersecurity breaches on the horizon for C-suite.
Source: FTI Consulting
9 Biggest Cybersecurity Future Trends to Watch Out For in 2023

1) Potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
2) IoT with 5G Network: The New Era of Technology and Risks
3) Mobile is the New Target
4) Targeted Ransomware
5) Rise of Automotive Hacking
6) Insider Threats
7) Automation and Integration
8) Cloud is also Potentially Vulnerable
9) State-Sponsored Cyber Warfare
7 Top Emerging Cybersecurity Trends For 2023
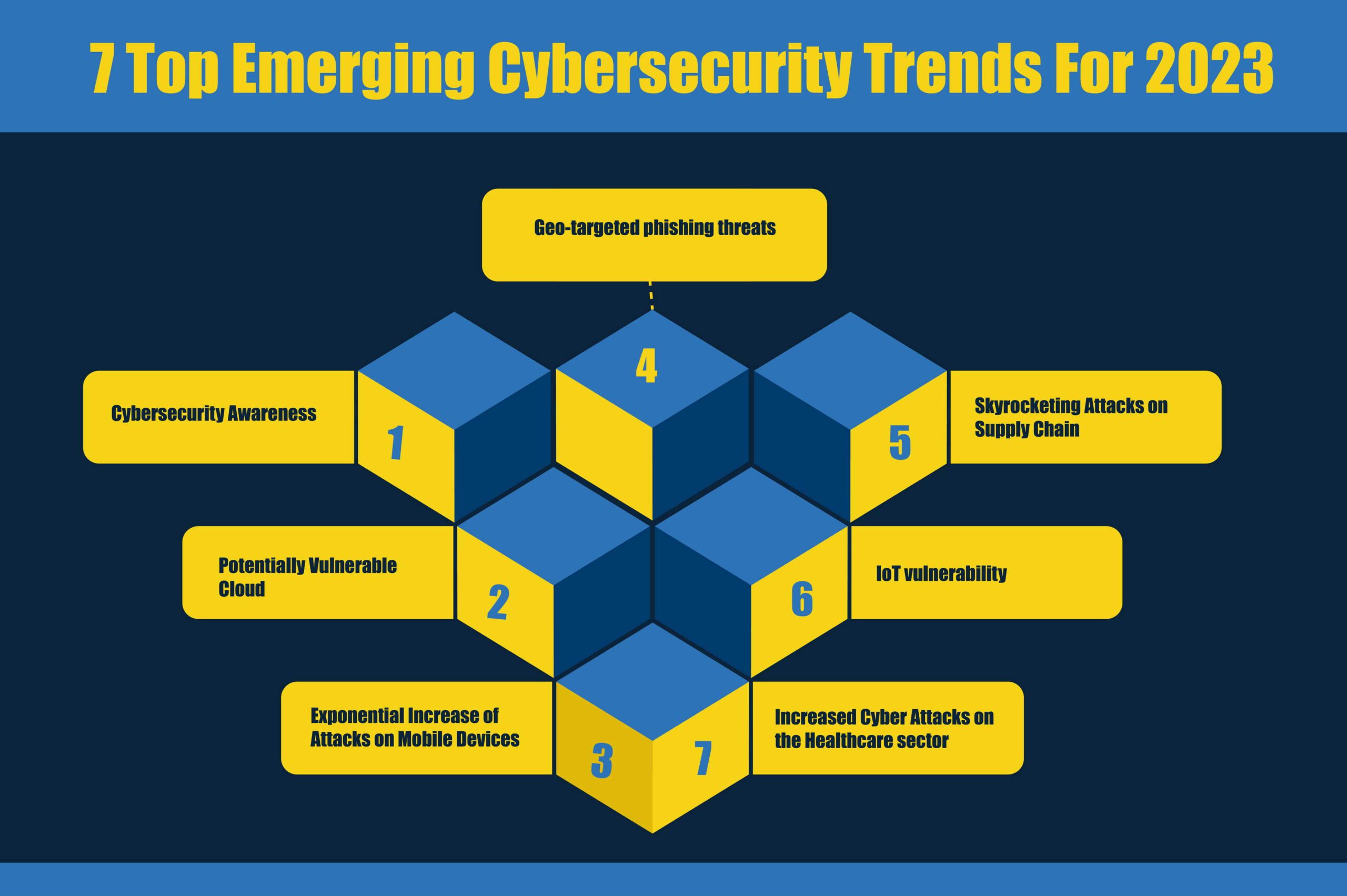
1) Cybersecurity Awareness
2) Potentially Vulnerable Cloud
3) Exponential Increase of Attacks on Mobile Devices
4) Geo-targeted phishing threats
5) Skyrocketing Attacks on Supply Chain
6) IoT vulnerability
7) Increased Cyber Attacks on the Healthcare sector
Top 8 Enterprise Security Trends to Look for in 2023

- Remote Working Security
- Digital Supply Chain Security Threats
- Persistence of Ransomware Attacks
- The Evolution of the Internet of Things and Related Security Concerns
- The Dominance of Cloud Computing Services and Related Threats
- More Sophisticated Social Engineering Attacks
- The Evolution of Multi-factor Authentication
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Enterprise Security
Gartner Strategic Cybersecurity Trends for 2023
- Composable Security
- Cybersecurity Platform Consolidation
- Cybersecurity Validation
- Enhancing People Management
- Human-Centric Security Design
- Identity Fabric Immunity
- Increasing Board Oversight
- Security Operating Model Transformation
- Threat Exposure Management
Cybersecurity Future Trends & Predictions For 2023 & Beyond
North American Cybersecurity Sub-Market, by Type, Through 2023 ($ millions)
| S.No. | Types of Submarkets | In ($ millions) | CAGR (%) |
| 1 | Network Security | $34,662.80 | 8.7 |
| 2 | Endpoint Security | $15,377.30 | 10.2 |
| 3 | Wireless Security | $11,254.70 | 10.9 |
| 4 | Content Security | $8,657.50 | 9.6 |
| 5 | Cloud Security | $6,868.20 | 12.8 |
| 6 | Application Security | $5,631.50 | 10.5 |
| (Source: BCC Research) Total | $82,452.00 | 9.8 |
Juniper Research survey says over 33 billion records will be stolen by cybercriminals in 2023 alone which is an increase of 175% in the last 5 years.
The US will become the primary target of data breaches with over half of all data breaches globally to occur by 2023 according to Juniper Research.
According to TechWire Asia, among all cyber breaches, damages due to ransomware threats are to exceed $30 billion by 2023
PWC’s 2023 Global Digital Trust Insights survey reveals that over 3,500 business, security and IT leaders in 60+ territories think that Cybersecurity has become a dynamic field, rapidly adjusting and shifting to keep pace with business inventiveness.
Analytics Insight estimates that 10 million new jobs will be required in the cybersecurity sector by 2023 growing at a CAGR of 25.3%.
The US Government has said it will launch a cybersecurity labeling program for consumer Internet of Things devices starting in 2023 in an effort to protect Americans from “significant national security risks.”
The budget will also provide the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) with $2.5 billion to “maintain critical cybersecurity capabilities”.
Cyberattacks like tech support fraud, identity theft attempts, and social engineering attacks are to watch for in 2023 and beyond.
38% of business leaders expect more serious attacks via the cloud in 2023, according to PWC.
The MEA Cybersecurity market size is expected to reach $31.82 billion by the year 2023 with a CAGR of 15.5%.
According to C-Suite, in 2023 the types of attacks expected to be prevalent are
- Business email compromise/account takeovers (33%)
- Ransomware (32%)
- Compromise of cloud management interfaces (31%)
- Hack-and-leak (30%)
- Third-party breach (29%)
- Compromise of the software supply chain (26%)
- IP theft (26%)
- IoT breaches (26%)
- DDoS (25%), and more.
Most executives believe that mobile devices will be the leading pathway for 41% of the attacks in 2023 followed by
- Email (40%)
- Cloud (38%)
- Web applications (37%)
- Human error/insider threat (37%)
- Third parties (34%)
- Endpoints (33%)
- Software supply chain (32%)
- Remote access portals (32%)
- IoT (29%) & OT (26%).
Google’s safe browsing service is protecting over 4 billion devices (VentureBeat, 2019).
91% of Cyber leaders working at IT companies fear that a catastrophic cyber attack is likely in the next two years which will affect their own organizations.
29% of business leaders strongly agree that more sector-wide regulatory enforcement would increase cyber resilience.
More than 39% of organization leaders agree that Cybersecurity is a key business enabler going forward.
The 2023 World Economic Forum survey says that 95% of business executives and 93% of cyber executives agree that cyber resilience is integrated into their company’s enterprise risk-management strategies.
Data Posture Security Management (DPSM) will be the future of cybersecurity, says Parandar Das, the co-founder and CEO of Sotero.
The future of Cybersecurity is based on the following events, says Solutions Review’s Security Experts:
John Chambers, the CEO of Cisco Systems Inc says “Architectural play that encompasses a 360-degree approach, from risk assessment and prevention to recovery shapes the future of cybersecurity”
Future of Cybersecurity According to Gartner
The category of Application security is identified as the second-fastest growing and is expected to rise over 25% and capture $7.5 billion in 2023 spending.
By 2025, 60% of enterprises will see cybersecurity risk as their main consideration when engaging in business with third parties.
The research firm expects the Security Services industry to garner over $76.5 billion in 2023 spending by organizations.
Up from less than 1% in 2021, 30% of nation-states will enact laws governing ransomware payments, fines, and discussions by 2025.
By the end of 2023, 5 billion people and more than 70% of the world’s GDP will be covered by legislation mandating businesses to respect consumers’ privacy rights.
70% of CEOs will demand a culture of organizational resilience by 2025 if they want their companies to survive converging risks from cybercrime, extreme weather, civil unrest, and political instability.
The technological research and consulting firm predicts that by 2023, 60% of enterprises will phase out most of their VPNs in favor of Zero Trust Network Access (ZNTA). Zero trust is a security protocol that maintains strict access controls by not trusting anyone blindly.
By 2025, 80% of businesses will adopt a strategy that unifies cloud, web, and private application access through an SSE platform from a single vendor.
By 2026, the employment contracts of 50% of C-level executives will include risk-related performance objectives.
Gartner predicts organizations will spend nearly $6.69 billion on cloud security in 2023, rising almost 27% year-over-year.
Cybersecurity Future Challenges and Opportunities
As we move forward to 2023, the security risks for the organizations will also continue to expand in tandem with their ongoing digital journeys.
Throughout 2023, the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR regulations will continue to greatly impact privacy policies.
In its report, Cisco predicts the total number of DDoS attacks worldwide will be 15.4 million by the end of 2023.
In 2023, the number of enterprises without access to affordable cyber insurance is expected to double according to Huntsman Security.
According to World Bank, By the year 2023, roughly USD 5.2 trillion in global value will be at risk from targeted cyberattacks.
The financial sector is on top, but so is healthcare, which will be increasingly under threat in 2023 as organizations in the U.S. face cyber-attacks of more than 713% over the next few years.
According to McKinsey, 85% of small and midsize businesses intend to increase IT security spending in 2023.
The Latin American cybersecurity market is anticipated to grow at an overall compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3 % and will be worth USD 20.65 Billion by 2023.
Spending on information security and risk management products and services will grow 11.3% in 2023, reaching more than $188.3 billion, according to Gartner.
Greater awareness of phishing and spoofing scams, improved password strength with a strong password generator, and some basic cyber health advice could help to prevent a huge chunk of attacks in 2023.
By the end of 2023, modern data privacy laws will cover the personal information of 75% of the world’s population.
According to LastPass, 50% of people use the same password for all their logins.
Cloud security is forecast to be the strongest category for growth in 2023 and there is a pressing need to improve it with innovative measures to combat cyber threats.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the global annual cost of cybercrime is predicted to reach $8 trillion in 2023. The breakup of damages due to cybercrime is given below:
What are the Future Cybersecurity Issues?
Predicting future cybersecurity issues is challenging because threats and vulnerabilities are constantly evolving as technology advances.
However, several trends and potential issues are likely to shape the future of cybersecurity.
Ransomware Evolution
Ransomware attacks are expected to become more sophisticated and targeted. Attackers may use AI and machine learning to automate their attacks and adapt to security defenses in real-time.
Additionally, ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure could have devastating consequences.
IoT Vulnerabilities
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices introduces new attack surfaces. Many IoT devices have weak security features, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Attacks on smart homes, industrial IoT, and critical infrastructure are all concerns.
5G and Edge Computing
The rollout of 5G networks and the adoption of edge computing will create new opportunities for cyberattacks. The increased speed and connectivity may lead to more vulnerabilities, especially in the early stages of implementation.
AI-Driven Attacks and Defenses
Cybercriminals will likely use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate attacks, discover vulnerabilities, and improve evasion tactics. Conversely, AI and ML will also play a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity defenses.
Supply Chain Attacks
Attackers may increasingly target software supply chains, injecting malicious code into widely-used software packages, or compromising hardware components. These attacks can have far-reaching consequences.
Biometric Data Theft
As biometric authentication becomes more widespread, the theft and misuse of biometric data (e.g., fingerprints, facial recognition) could become a significant issue. Biometric data, once compromised, cannot be changed like passwords.
Quantum Computing Threats
While still in its infancy, quantum computing has the potential to break current encryption algorithms. Preparing for the post-quantum cryptography era will be essential.
Regulatory Challenges
Compliance with evolving data protection and privacy regulations (such as GDPR, CCPA, and new laws that may emerge) will continue to be a challenge for organizations.
Social Engineering and Phishing
Human-based attacks, such as social engineering and phishing, are likely to persist and become more sophisticated. Attackers will use psychological tactics to manipulate individuals into reveal sensitive information.
Nation-State Cyber Warfare
Nation-state actors engaging in cyber warfare will remain a significant concern. Attacks on critical infrastructure, espionage, and disinformation campaigns can have far-reaching consequences.
Cybersecurity Workforce Shortage
The shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals is expected to persist, making it challenging for organizations to defend against threats effectively.
Cloud Security Concerns
As more organizations migrate to the cloud, securing cloud infrastructure and services will be a top priority. Misconfigured cloud resources can expose sensitive data to the internet.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies like blockchain, quantum communication, and augmented reality could introduce novel cybersecurity challenges as they become more integrated into daily life and business operations.
To address the above future cybersecurity issues, organizations and cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant, invest in training and technology, and adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
Collaboration between the public and private sectors, as well as international cooperation, will also be crucial in mitigating these threats.
Top Investing Cybersecurity Segments for American Companies in 2023

- Advanced Malware Sandbox (AMS)
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Mitigation
- Endpoint Security
- Identity Access Management (IAM)
- Managed Security Services (MSS)
- Network Access Control (NAC)
- Security Information & Event Management (SIEM)
- Unified Threat Management (UTM) & Next Generation Firewall (NGFW)
- Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Web & Email Content Security
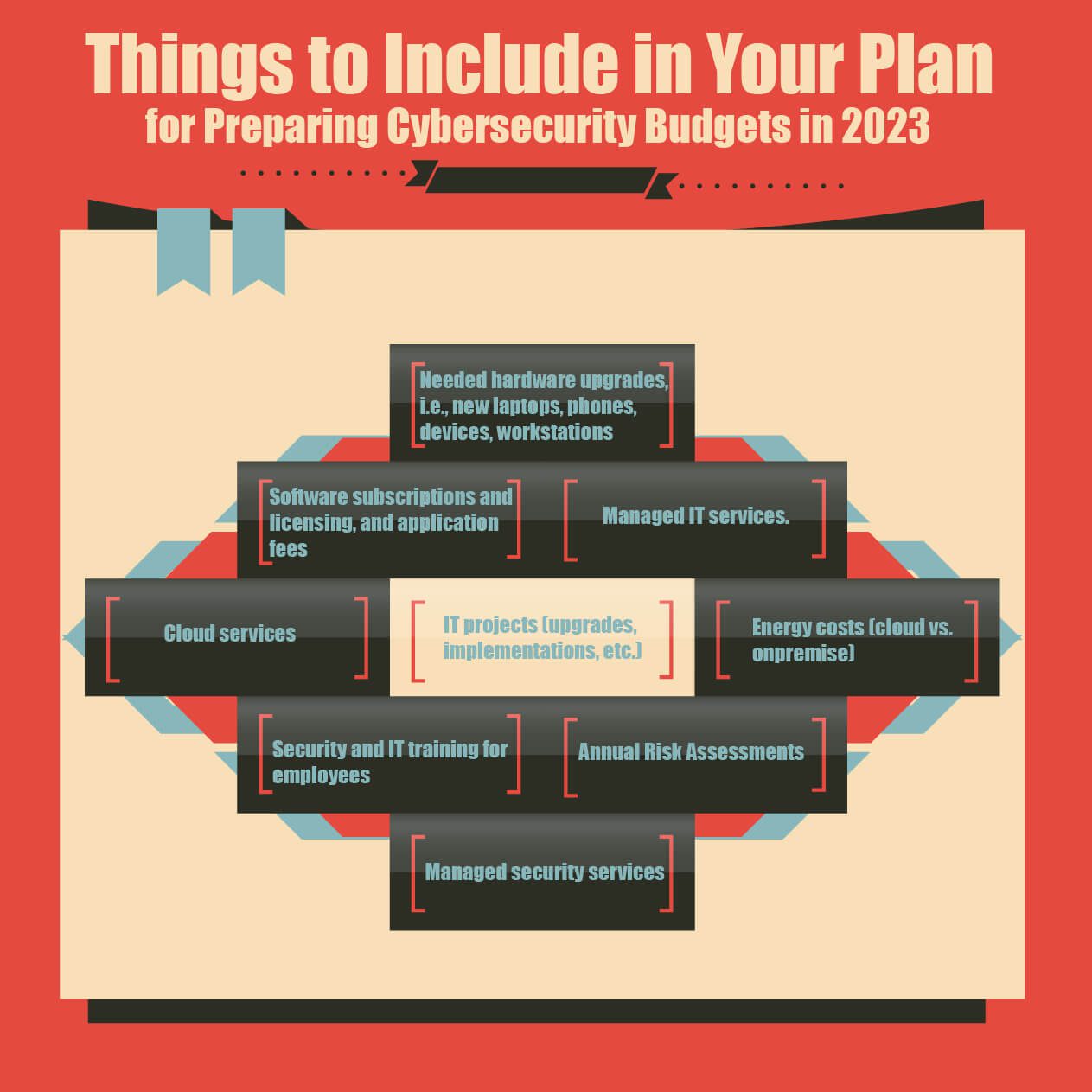
Things to Include in Your Plan for Preparing Cybersecurity Budgets in 2023
Cybersecurity Industry Trends in 2022

1) Rise of Automotive Hacking
2) Potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) 3) Mobile is the New Target
4) Cloud is Also Potentially Vulnerable
5) Data Breaches: Prime target
6) IoT with 5G Network: The New Era of Technology and Risks
7) Automation and Integration
8) Targeted Ransomware
9) State-Sponsored Cyber Warfare
10) Insider Threats
How Big Will Cybersecurity Be in the Future?
Cybersecurity is expected to continue growing in importance and size in the future. Several factors contribute to this trend are given below.
Increasing Reliance on Technology
As society becomes more digitally connected, we rely on technology for nearly every aspect of our lives, from communication to finance to healthcare.
This increasing digitization makes us more vulnerable to cyber threats, necessitating stronger cybersecurity measures.
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and diverse. Attackers are developing new techniques and tools to breach security systems, steal data, and disrupt services. This dynamic threat landscape requires ongoing investment in cybersecurity.
Data Protection Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are enacting stricter data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Compliance with these regulations requires organizations to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data.
Internet of Things (IoT) Growth
The proliferation of IoT devices adds millions of connected endpoints to networks, increasing the attack surface for cybercriminals. Securing these devices and networks is a significant challenge that will drive the demand for cybersecurity expertise.
Remote Work Trends
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to remote work, making organizations more vulnerable to cyberattacks. As remote work becomes a permanent fixture in many industries, cybersecurity measures will be crucial to safeguard remote environments.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
While AI and automation can enhance cybersecurity, they also introduce new risks. Cybersecurity professionals will need to develop and implement AI-driven defenses while guarding against AI-powered attacks.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap
There is a growing shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals. As organizations recognize the need for stronger security measures, they will continue to invest in training and hiring cybersecurity experts.
Economic Impact of Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks can have severe economic consequences, causing financial losses and damaging reputations. The high cost of cyberattacks will drive organizations to prioritize cybersecurity.
Nation-State Threats
State-sponsored cyberattacks are a growing concern, with governments engaging in cyber espionage, disruption, and warfare. This will lead to increased investments in national and international cybersecurity efforts.
Future of Cybersecurity Career
Although the demand for cybersecurity professionals will continue to rise, there are still many open positions.
In fact, a report released by Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that the most in-demand cybersecurity skills will be database administrators, who have the potential to earn $78,000 a year.
The demand for cybersecurity professionals has grown due to the increased number of cyberattacks and the widespread adoption of technology.
The cost and complexity associated with these attacks make it difficult for companies to protect themselves without hiring experts.
Furthermore, as corporate systems become increasingly interconnected, cyberattacks become increasingly difficult to prevent.
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is predicted to be 20% over the next decade. As a result, cybersecurity may remain one of the fastest-growing careers for years to come.
According to Payscale.com, the lowest 10% of earners in this field make anywhere from $32,000 to $69,000 per year while the highest 10% earn upwards of over $130,000 each year.
Future of Cybersecurity Jobs
- Cybersecurity career growth is projected to rise exponentially in the year 2023.
- The demand for digital skills will be accelerated considerably in 2023.
- Technology professionals with advanced skills will find themselves in a very favorable position when it comes to job opportunities in 2023.
- Coding knowledge of C#, C++, Angular, Node.js, AWS, Google Cloud Platform and Azure will continue to see an intense demand in 2023 and beyond.
- Application Development Security (ADS) and Cloud Security (CS) are the two fastest-growing skill areas in cybersecurity, with estimated growth of 164% and 115%, respectively.
- By mastering modern software delivery processes like DevOps, developers can recession-proof themselves and demonstrate how they can add value and directly address business challenges
- According to Cybersecurity Ventures, there will be 3.5 million Cybersecurity job openings by 2025 and unfilled jobs grew by 350 percent at the same time.
- Global recruiting consultancy Michael Page states that India alone is expected to generate more than 1.5 million jobs in the cybersecurity sector by 2025.
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that by 2023, there will be around 1 million cybersecurity job openings across the country. Information Security Analyst jobs are projected to grow 35 percent from 2021 to 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations.
- A national campaign launched by Microsoft in the U.S. community colleges to help place almost 250,000 skilled professionals into the cybersecurity sector by 2025.
- Global Cyber publisher, Cybersecurity Ventures expects that women will represent 30 percent of the global cybersecurity workforce by 2025, and will increase to 35 percent by 2031.
- Cybersecurity is an ever-growing industry and is expected to grow by 11% in 2023 and 20% by the year 2025.
Highest Paying Cybersecurity Jobs in 2023 with the Median Salary
Cybersecurity in the United States
The United States has been experiencing an increase in cybersecurity breaches. The US is also the world’s most targeted country for cyberattacks due to its high profile and large population.
The K12 Cybersecurity Act of 2021 would require schools to have adequate cybersecurity protections for students, teachers and staff.
According to the Cybersecurity Act of 2021, school districts should be required to:
Cybersecurity Future Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be a major component of all Cybersecurity
Over the last few years, Artificial Intelligence has, as expertise, come to fruition in various industries.
Nowadays, AI and machine learning algorithms can be used to computerize tasks, crunch data, and make decisions far more quickly than an individual ever could.
But, new technologies, including AI, intrinsically create cybersecurity risks as possible exploits are badly understood at the time of release.
This means that, with more businesses relying on machine learning for mission-critical processes, AI systems certainly become the main target for hackers.
In response, future cybersecurity software & employees will be forced to develop an automated threat detection system to counter the surging threat landscape such as sophisticated cyber-attacks and data breaches.
5 Biggest Artificial Intelligence (AI) Trends In 2023 For Cybersecurity

- The Ongoing Democratization of AI
- Generative AI
- Ethical and Explainable AI
- Augmented Working
- Sustainable AI
On-demand access to universal data & information platforms
Mobile platforms, remote work, & other shifts gradually hinge on high-speed access to universal and huge data sets, exacerbating the possibility of a breach. The market for web hosting services is projected to make $183.18 billion by 2026.
Organizations gather far more data about clients—the whole thing from financial transactions to electricity consumption to social media views—to recognize and influence buying behavior and more efficiently forecast demand.
In 2020, on average, each person on Earth created 1.7 megabytes of data every second.
With the greater significance of the cloud, enterprises are more and more responsible for storing, handling, and protecting these data & for meeting the challenges of unstable data volumes.
Third-party risks and threats
As companies keep on ramping up their efforts and accepting digital technologies, many turn to third parties, outsourcing some IT & security support requirements.
As we’ve discussed before, reliance on third parties increases cyber security risks, mainly for companies that do not have a policy in place for handling these risks.
Raids on Cloud Services
In the past few years, several businesses have adopted cloud-based computing services that allow users to get software applications, data storage, & other services through an internet connection rather than depending on physical infrastructure.
Embracing this expertise comes with lots of benefits such as reduced operational costs and better efficiency.
Although choosing such systems can be extremely beneficial to organizations, they have also become the target of cyber threats.
If these systems are not correctly configured or retained, attackers are more possibly to be able to exploit vulnerabilities in the systems’ security and get access to responsive information.
This is particularly significant, seeing that many of today’s organizations depend on cloud services as workers work remotely.
Higher Risk of Malware Attacks
The future of cybersecurity also holds lots of malware attacks – but not the type we have seen in recent years! It is no secret that attackers are using ransomware to attack organizations, businesses, and individuals all over the globe.
But, most of these attacks exploit recognized vulnerabilities or “traditional” methods, which means they can be effortlessly prevented – for instance, by updating security software frequently, running red team safety testing, & using anti-virus programs.
The future of cybersecurity holds sophisticated malware attacks that will be very tough to stop.
Hackers will be competent to use artificial intelligence systems to make new methods of attacking computer networks & bypassing security systems.
They will carry on using social engineering techniques to trick users into providing them with entrée to their computers and networks or target IoT devices.
As technology grows, we will see even more inventive ways to conduct cyber attacks, which means cybersecurity specialists should develop new ways to defend against them.
It is not possible to predict how far this might go – but it is clear that this fight between hackers & security specialists will go on for many years to come.
Attacks on the Healthcare Sector
Failing to battle cyber threats in the healthcare division exposes several individuals & organizations to all sorts of liability & security issues. This led to health organizations and hospitals investing further in cybersecurity.
In 2019, the worth of the healthcare cybersecurity marketplace was $9.78 billion & this is estimated to rise to $33.65 billion by 2027.
Taking into account the pandemic of COVID-19 in the healthcare division, experts expect that the market might reach $125 billion by 2025.
Use of internet-of-things (IoT)
In the coming five years, the use of IoT technology will boost as more people utilize it in their everyday lives. According to a report from IoT Analytics, there were 10 billion linked devices in the year 2019 & we could see it three times to $30.9 billion by the year 2025.
Although connecting to networks & other devices that access very sensitive information, IoT devices carry on having fairly weak safety controls.
Several businesses already struggle to give additional safety measures that will keep these devices protected.
How Big Data Can Drive The Future of Cybersecurity?
Big data has the potential to significantly impact the future of cybersecurity in several ways:
Threat Intelligence: Big data can help identify patterns and detect irregular patterns in vast amounts of data, enabling organizations to identify potential cyber threats and develop solutions to mitigate them.
By collecting and analyzing data from system events, user behavior and network logs cybersecurity professionals will be able to interpret valuable insights of emerging threats and improve their ability to detect and respond to attacks.
Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: It provides the necessary inputs for training and deploying machine learning algorithms that can automatically analyze and classify cyber threats.
By leveraging large datasets, machine learning models can learn from historical attack data and identify new attack vectors and patterns that may go unnoticed by traditional security solutions.
These models can continuously evolve and improve their accuracy over time, enhancing the overall effectiveness of cybersecurity defenses.
Anomaly Detection and Behavioral Analysis: Big data analytics can help establish baselines of normal behavior for various systems, networks, and users.
By continuously monitoring and analyzing data from these sources, organizations can identify deviations from normal behavior that may indicate potential security breaches.
This approach, known as anomaly detection, can detect sophisticated attacks that evade traditional signature-based defenses.
Real-time Monitoring and Incident Response: It also enables organizations to collect and process large volumes of security-related data in real time.
By monitoring network traffic, system logs, and other security events, organizations can identify and respond to security incidents promptly.
Real-time monitoring combined with advanced analytics allows for early detection and faster response, minimizing the impact of cyberattacks.
Forensics and Investigation: Big data can also play a crucial role in post-incident analysis and forensic investigations.
Threat Hunting: Big data analytics can empower cybersecurity professionals to proactively search for potential threats and vulnerabilities within their networks.
By aggregating and analyzing large datasets, security teams can identify indicators of compromise and uncover hidden patterns that may indicate the presence of advanced persistent threats (APTs).
This proactive approach allows organizations to stay one step ahead of attackers and take preventive measures before an attack occurs.
What is the Future of Cybersecurity in 2030?
According to World Economic Forum, 7 trends that will shape the future of cybersecurity by 2030 to face cyber threats are:
- Sovereignty and shifting power dynamics
- Metaverse uncertainty
- Pull and push between regulatory experiments and the future of privacy
- Downsides (and limited upsides) of Internet fragmentation
- The double-edged sword of AI and ML technologies
- The worsening crisis in trust online
- Progress in cybersecurity, but access must be widened

Adoption of Cybersecurity
Cyber-attacks are global, and hackers can infringe on government agencies. The National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) has warned businesses and citizens that use router-like network infrastructure devices worldwide.
The goal is to lay the groundwork for future attacks on critical infrastructure such as power plants and power grids.
Even small organizations are being threatened if they do not keep their security strong. Computer viruses and phishing were particularly prevalent, but 12% faced hacking, and 7% – multiple of 15 businesses – suffered data breaches.
The importance of cybersecurity is growing. Fundamentally, our society is more technologically dependent than ever before, and there is no sign that this trend will diminish.
Personal data that could be the result of identity theft is now posted to the public on our social media accounts.
Conclusion
Due to the stable progress in the field of expertise, the future of cybersecurity looks promising.
We will see more improvements that will make it simpler & safer to run a business online. But, it also implies an increased difficulty of malware & cyber attacks.
Though there is no way to recognize precisely what the future of cybersecurity holds, it will possibly be full of innovation and development.
As technology advances, so does the need for improved cybersecurity solutions – and we will possibly see lots of new ones in the next few years.
So, businesses must upgrade their safety systems to be competent to protect themselves against even the most sophisticated cyber attacks.
We will also see ample new tools that will let businesses evaluate the risks better and defend their networks & data.
Cybersecurity specialists should continue working on superior tools & technologies to make sure companies have the resources they need to withstand the most complex cyber-attacks.
FAQs
What is the Future Growth of Cybersecurity?
In the future, cybersecurity will be a top priority for every company, and the cybersecurity industry is expected to grow by 44% in the next five years.
As the industry grows, it will require more professionals and companies to hire cybersecurity professionals.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 14% increase in employment for electrical engineers, a 12% jump for computer and information systems managers, and an average 4% increase for computer programmers between 2016–2026.
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is expected to grow as companies grow in size and scale, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics estimating an increase of about 5% for employment in small-sized businesses over this period.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there are expected to be 1.5 million cybersecurity jobs in the United States by 2024, but not all these jobs will be available at large corporations.
The average salary of a cybersecurity engineer is $94,000. The median annual salary for cybersecurity engineers is $83,000.
What are 3 Important Components of Cybersecurity?
Access Control: Access control is fundamental in cybersecurity. It involves mechanisms and policies that limit and manage who can access specific resources, systems, or data.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, like the internet. They filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of security rules.
Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keeping software, operating systems, and applications up to date with the latest security patches and updates is crucial.


