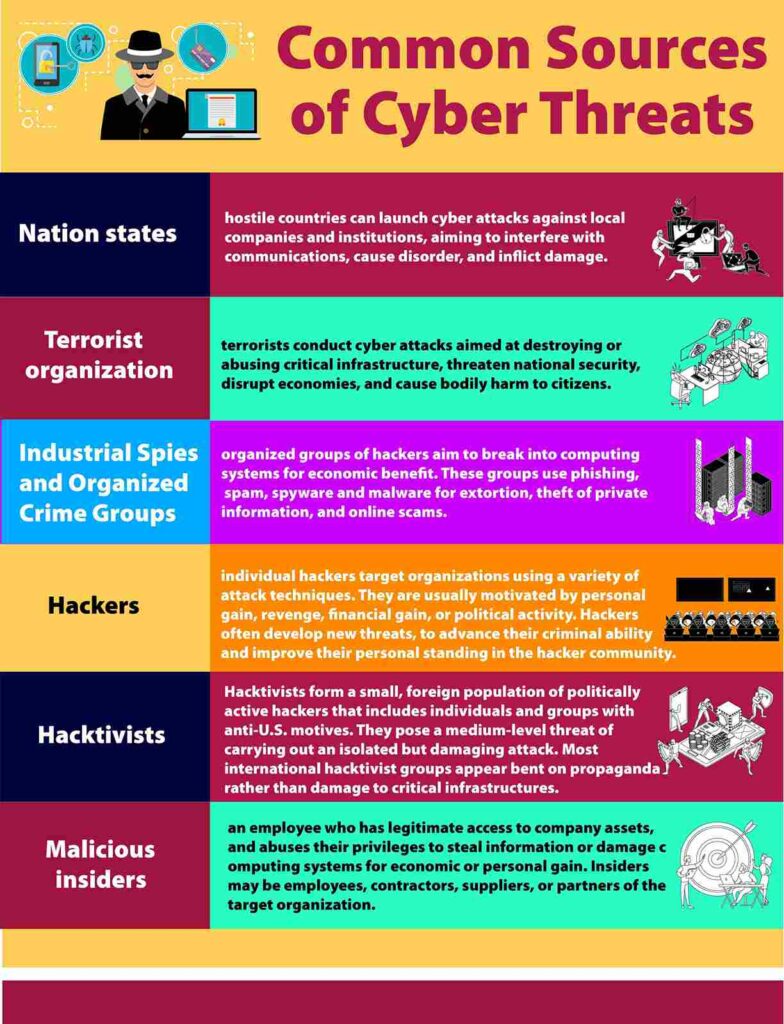
Common Sources of Cyber Threats
Nation states—hostile countries can launch cyber attacks against local companies and institutions, aiming to interfere with communications, cause disorder, and inflict damage.
Terrorist organizations—terrorists conduct cyber attacks aimed at destroying or abusing critical infrastructure, threatening national security, disrupting economies, and causing bodily harm to citizens.
Industrial Spies and Organized Crime Groups—organized groups of hackers aim to break into computing systems for economic benefit. These groups use phishing, spam, spyware and malware for extortion, theft of private information, and online scams.
Hackers—individual hackers target organizations using a variety of attack techniques. They are usually motivated by personal gain, revenge, financial gain, or political activity.
Hackers often develop new threats, to advance their criminal ability and improve their personal standing in the hacker community.
Hacktivists- Hacktivists form a small, foreign population of politically active hackers that includes individuals and groups with anti-U.S. motives.
They pose a medium-level threat of carrying out an isolated but damaging attack. Most international hacktivist groups appear bent on propaganda rather than damage to critical infrastructures.
Malicious insiders—an employee who has legitimate access to company assets, and abuses their privileges to steal information or damage computing systems for economic or personal gain. Insiders may be employees, contractors, suppliers, or partners of the target organization.
Source: US-CERT (CISA)

