With the rise in gizmos and high-end technology in the current era, cybersecurity has become crucial for any business as it contains sensitive data such as passwords, identity, and other confidential information.
Cybersecurity uses technology, techniques, and policies to defend against cyberattacks on systems, networks, programs, devices, and data.
Its goal is to limit the risk of cyber assaults and guard against unauthorized exploitation of systems, networks, and technology. Individuals and businesses use it to prevent illegal access to data centers and other digital systems.
Table of Contents
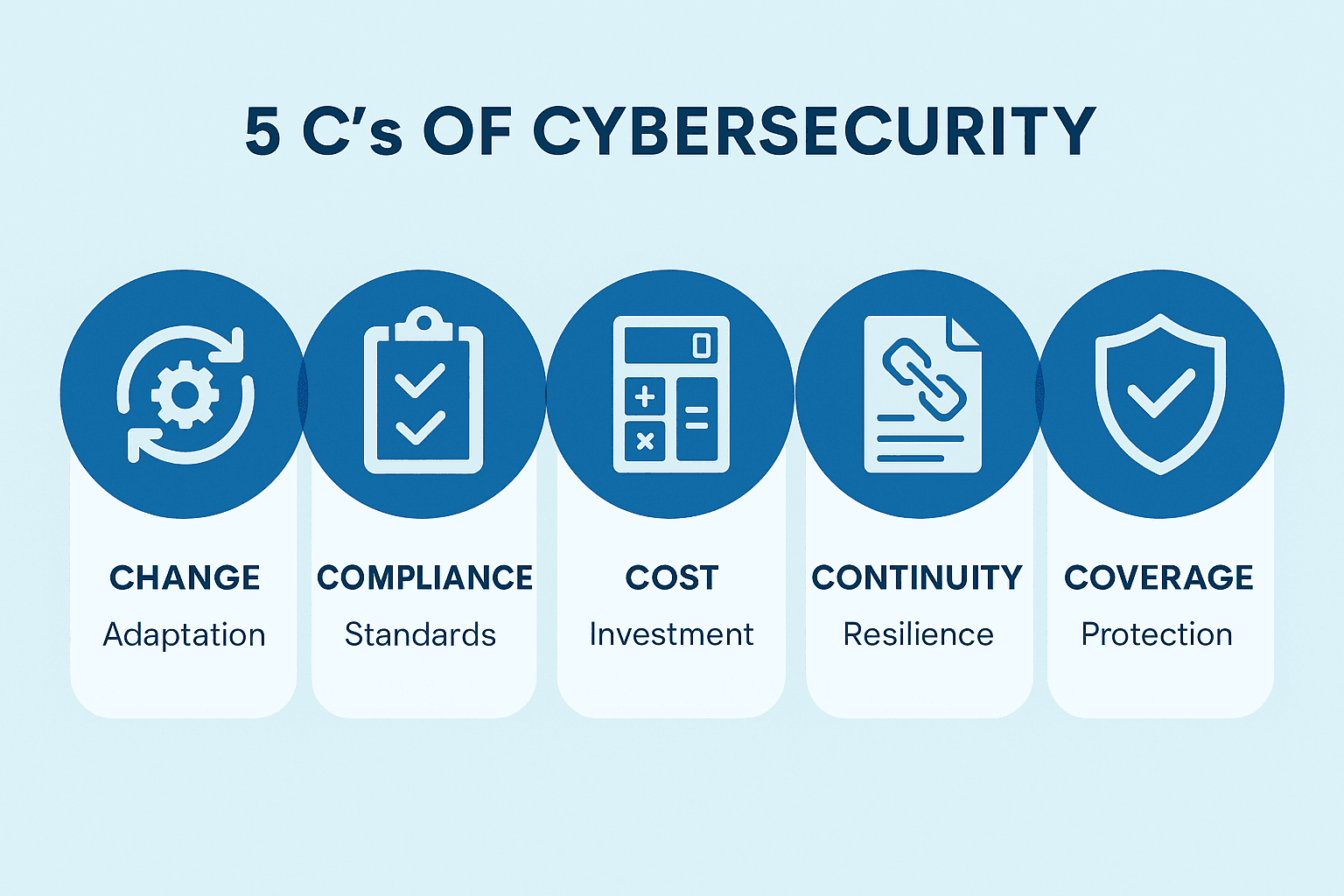
5 C’s of Cybersecurity
The 5 C’s of Cybersecurity represent key areas organizations and individuals should focus on to maintain a strong security posture.
1. Change
With constant changes in technologies and guidelines, managers and team leaders are forced to remain vigilant at all times.
Professional managers are now creating an organization of systems and infrastructure that can effectively respond to threats and seize opportunities at a rapid speed.
2. Compliance
Corporate governance, ownership, risk management, and compliance with legal guidelines are the focal point of many companies.
Nevertheless, it is not enough to demonstrate your purpose to comply with rules and regulations. Companies should regularly examine and report how they can comply with these regulations.
Concerning physical network security, certain compliance violations may result in extensive data breaches, economic loss, denial of services, and even damage to employees or visitors.
Using traditional physical security, i.e., client and server architecture, will further threaten company assets and confidential information.
A standard and basic enterprise installation may comprise more than a dozen computers with access to security controls and very sensitive and confidential information.
Assuring how to manage access to these resources and which protocols should be followed is not a straightforward task and may require years of experience.
SaaS architecture can effectively implement compliance regulations and regular audits much easier by offering centralized functions to set standards and tools for tracking and reporting compliance.
As the SaaS solution database is centralized in the organization framework, the budget for carrying out the adherence audits is considerably reduced.
Many software as service providers can give evidence of internal controls certified by independent auditors, thereby excluding the need for an external individual to handle these costs.
3. Cost
The survival of any business depends on its capacity to provide life-long value to its customers. It is not easy to provide high credibility without considering the cost of the enterprise.
The software and hardware purchased carry enough capacity to meet current and future needs. These devices use internal resources for installation, power supply, and regular maintenance.
Quite frequently, excess resources occur in the host computers and within each device functioning the client software.
4. Continuity
Organizations often spend thousands of dollars on their security platforms using standby workstations, high-end backup power supplies, and disaster recovery zones for their staff and employees.
Such measures are fairly traditional and expensive, and major disasters may contest internal computer networks. So it’s only sensible to cover the safety models holistically in an organization.
5. Coverage
Organizations usually find the most effortless way to boost profitable growth using geographic expansion. There are numerous challenges, risks, and expenses that come along with expansion, and they come at a cost.
They can also be extremely costly or inexpensive, depending on various factors that might affect an organization’s credibility in the long run.